Dear Guests,
Welcome to ICOASE 2018!
You can use this forum for any discussions for the ICOASE 2018. You can create topics or answer questions either if you are registered or as a guest (without registration).
If you want you can create a new topic if such a topic does not exist (Not discussed before), or reply to any topic if you have a reasonable answer so that others can get your idea.
Feel free to ask any question and in any language!
Thanks for your cooperation.
Transformer4U: Power Transformer Guide & Resources -
Quote from Guest on January 9, 2026, 6:13 pmUnderstanding Power Transformers and Current Transformers: A Complete Guide
In the world of electrical engineering, power transformer and current transformers play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and safe distribution of electrical energy. Whether you are an aspiring electrical engineer or a seasoned professional, understanding these devices is essential for designing, maintaining, and troubleshooting electrical systems.
What is a Power Transformer?
A power transformer is an electrical device used to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Its primary purpose is to step up or step down voltage levels while maintaining the frequency of the current. Power transformers are commonly used in power generation, transmission, and distribution systems.
Key Functions of Power Transformers:
Voltage Conversion: Step up voltage for efficient long-distance transmission and step down voltage for safe usage in homes and industries.
Energy Efficiency: Minimize energy loss during transmission.
System Protection: Ensure stability and prevent overloads in electrical networks.
Types of Power Transformers:
Step-Up Transformers: Increase voltage from low to high levels.
Step-Down Transformers: Reduce high voltage to lower levels for industrial or residential use.
Isolation Transformers: Provide electrical isolation while transferring energy between circuits.
What is a Current Transformer?
A current transformer (CT) is a type of instrument transformer used to measure high current values safely. It reduces high currents to a lower, standardized level, making them compatible with measurement instruments and protective relays.
Applications of Current Transformers:
Monitoring electrical systems for accurate current measurements.
Providing input to protective relays in case of overload or short circuits.
Ensuring safety for personnel and equipment by isolating high voltage circuits.
Advantages of Using Current Transformers:
High accuracy in measuring large currents.
Enhanced safety in high-voltage systems.
Compact and cost-effective design for industrial and commercial applications.
Best Practices for Transformer Maintenance
Proper maintenance of both power transformers and current transformers ensures longevity and reliability. Here are some essential tips:
Regular Inspections: Check for leaks, overheating, and unusual noises.
Oil Testing: Monitor transformer oil for moisture content and dielectric strength.
Load Management: Avoid overloading to prevent damage and reduce energy loss.
Cleaning: Keep transformers free from dust and debris to maintain efficiency.
Troubleshooting Common Transformer Issues
Even well-maintained transformers can face issues. Some common problems include:
Overheating: Often caused by overloading or poor ventilation.
Short Circuits: Can occur due to insulation failure or moisture ingress.
Noise and Vibration: May indicate loose components or core issues.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent costly downtime and ensure smooth operation.
Conclusion
Understanding power transformers and current transformer is vital for anyone involved in electrical engineering or industrial power systems. By focusing on design principles, proper maintenance, and troubleshooting techniques, you can enhance the efficiency, safety, and reliability of electrical networks.
Understanding Power Transformers and Current Transformers: A Complete Guide

In the world of electrical engineering, power transformer and current transformers play a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and safe distribution of electrical energy. Whether you are an aspiring electrical engineer or a seasoned professional, understanding these devices is essential for designing, maintaining, and troubleshooting electrical systems.
What is a Power Transformer?
A power transformer is an electrical device used to transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. Its primary purpose is to step up or step down voltage levels while maintaining the frequency of the current. Power transformers are commonly used in power generation, transmission, and distribution systems.
Key Functions of Power Transformers:
Voltage Conversion: Step up voltage for efficient long-distance transmission and step down voltage for safe usage in homes and industries.
Energy Efficiency: Minimize energy loss during transmission.
System Protection: Ensure stability and prevent overloads in electrical networks.
Types of Power Transformers:
Step-Up Transformers: Increase voltage from low to high levels.
Step-Down Transformers: Reduce high voltage to lower levels for industrial or residential use.
Isolation Transformers: Provide electrical isolation while transferring energy between circuits.
What is a Current Transformer?
A current transformer (CT) is a type of instrument transformer used to measure high current values safely. It reduces high currents to a lower, standardized level, making them compatible with measurement instruments and protective relays.
Applications of Current Transformers:
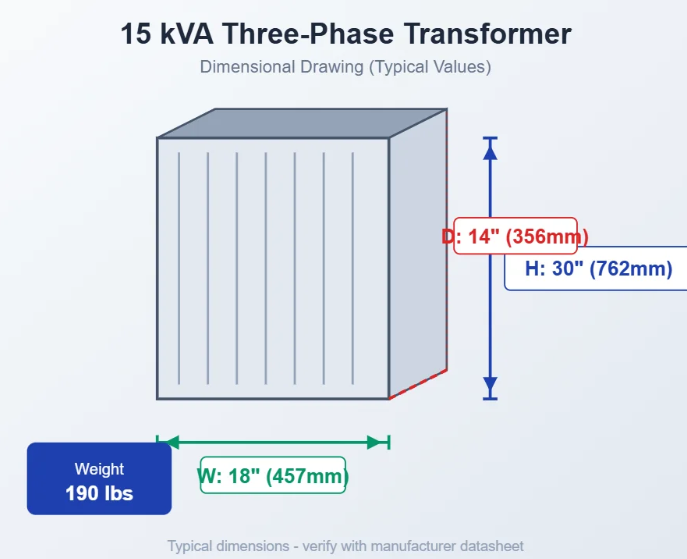
Monitoring electrical systems for accurate current measurements.
Providing input to protective relays in case of overload or short circuits.
Ensuring safety for personnel and equipment by isolating high voltage circuits.
Advantages of Using Current Transformers:
High accuracy in measuring large currents.
Enhanced safety in high-voltage systems.
Compact and cost-effective design for industrial and commercial applications.
Best Practices for Transformer Maintenance
Proper maintenance of both power transformers and current transformers ensures longevity and reliability. Here are some essential tips:
Regular Inspections: Check for leaks, overheating, and unusual noises.
Oil Testing: Monitor transformer oil for moisture content and dielectric strength.
Load Management: Avoid overloading to prevent damage and reduce energy loss.
Cleaning: Keep transformers free from dust and debris to maintain efficiency.
Troubleshooting Common Transformer Issues
Even well-maintained transformers can face issues. Some common problems include:
Overheating: Often caused by overloading or poor ventilation.
Short Circuits: Can occur due to insulation failure or moisture ingress.
Noise and Vibration: May indicate loose components or core issues.
Addressing these issues promptly can prevent costly downtime and ensure smooth operation.
Conclusion
Understanding power transformers and current transformer is vital for anyone involved in electrical engineering or industrial power systems. By focusing on design principles, proper maintenance, and troubleshooting techniques, you can enhance the efficiency, safety, and reliability of electrical networks.
Quote from Guest on January 16, 2026, 12:19 pmThis design is steller! You most certainly know how to keep a reader entertained.
Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to
start my own blog (well, almost...HaHa!) Great job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it.
Too cool! https://cryptobossnewar.top/
This design is steller! You most certainly know how to keep a reader entertained.
Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to
start my own blog (well, almost...HaHa!) Great job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it.
Too cool! https://cryptobossnewar.top/
Quote from Guest on January 19, 2026, 6:52 pmHurrah, that's what I was looking for, what a data! present here at this webpage, thanks admin of this site. https://nowostnik.ru/forums/topic/chat-ruletka-bez-czenzury/
Hurrah, that's what I was looking for, what a data! present here at this webpage, thanks admin of this site. https://nowostnik.ru/forums/topic/chat-ruletka-bez-czenzury/
Quote from Guest on February 20, 2026, 5:05 amThis article will help the internet viewers for setting up new weblog or even a weblog from start to end. https://avyc.io/thaddeuskujaws
This article will help the internet viewers for setting up new weblog or even a weblog from start to end. https://avyc.io/thaddeuskujaws
If you want to register to the website so that your name is visible to others, please follow the following steps:
- Click on the register
- Enter a valid email to be registered with
- Check your entered email to verify your email address and set a new password for you
- Goto Forum and log-in with your email and password
- Ask your question to the forum
Kind regards,

